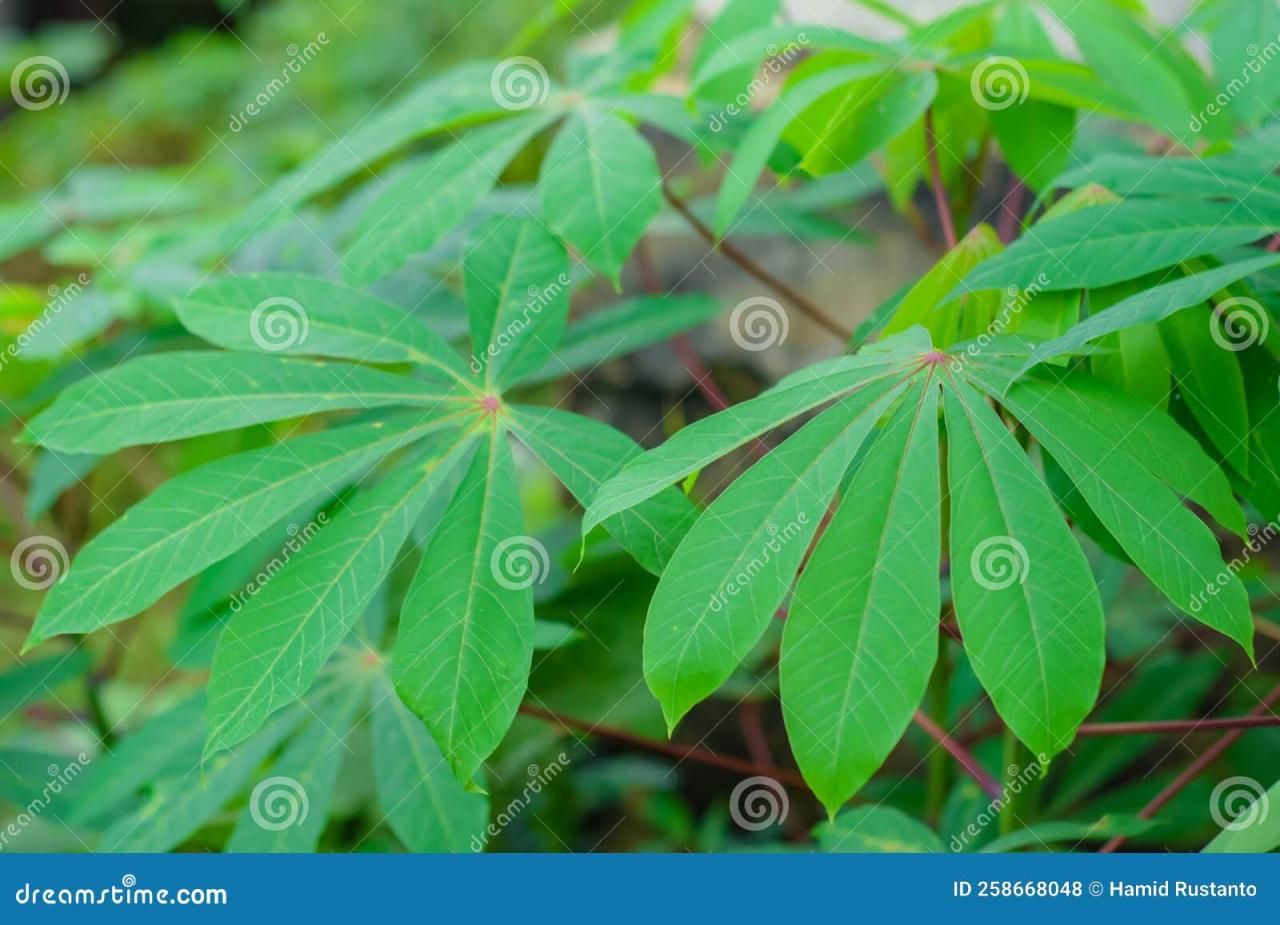
Cassava Leaf Magic: How to Cultivate and Enjoy This Nutritious Green for Optimal Results – the phrase itself conjures up images of vibrant green leaves brimming with health benefits. Beyond its culinary versatility, cassava leaf holds a rich history and offers a wealth of nutritional value.
This humble green has been a staple in many cultures for centuries, providing sustenance and contributing to a healthy lifestyle.
From its origins in South America, cassava leaf has spread globally, finding its place in diverse cuisines. Its unique flavor profile and nutritional richness have captivated chefs and home cooks alike, inspiring countless recipes and culinary traditions. But beyond its culinary appeal, cassava leaf boasts an impressive array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making it a nutritional powerhouse.
Introduction to Cassava Leaf Magic

Cassava leaves, often overlooked as a culinary ingredient, are a nutritional powerhouse brimming with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These leafy greens, commonly known as “cassava tops” or “manihot leaves,” offer a range of health benefits and culinary versatility.
Cassava leaves are a rich source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as iron, calcium, and folate. They are also high in fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes satiety. Furthermore, their antioxidant properties help protect the body against free radical damage, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Culinary Versatility of Cassava Leaves
Cassava leaves are a staple ingredient in many African and South American cuisines. They can be cooked in various ways, including steaming, boiling, frying, and sautéing. Their mild, slightly bitter flavor pairs well with a variety of seasonings and spices, making them a versatile addition to soups, stews, salads, and stir-fries.
Cassava leaves can be used to create a wide array of dishes. For instance, in West Africa, they are often prepared as a flavorful soup called “Egusi Soup” or “Okra Soup,” adding a unique texture and taste. In South America, they are frequently used in “Acaraje,” a popular street food consisting of black-eyed peas and cassava leaves.
Historical Significance of Cassava Leaf Consumption
The consumption of cassava leaves has a long and rich history, dating back centuries in various parts of the world. Indigenous cultures in South America and Africa have traditionally utilized these leaves as a vital source of nutrition and sustenance.
Historically, cassava leaves have played a crucial role in preventing malnutrition and supporting the health of communities. Their abundance and nutritional value have made them a reliable food source, particularly during times of food scarcity.
Cultivating Cassava Leaves for Optimal Growth
Cassava leaves, a nutritional powerhouse, can be a valuable addition to your diet. To maximize your harvest and enjoy the benefits of these nutrient-rich greens, understanding the optimal growing conditions and cultivation practices is essential. This section delves into the intricacies of cultivating cassava leaves for optimal growth, ensuring a bountiful and healthy yield.
Ideal Climate and Soil Conditions
Cassava thrives in warm, tropical climates with ample sunlight. It is a resilient plant that can tolerate a range of soil conditions, but prefers well-drained, sandy loam soil with a pH of 5.5 to 6.5.
- Temperature:Cassava thrives in temperatures between 25°C and 35°C (77°F and 95°F).
- Sunlight:Cassava requires at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily for optimal growth.
- Soil Drainage:Good drainage is crucial to prevent root rot, a common problem in cassava cultivation.
- Soil pH:A slightly acidic to neutral soil pH is ideal for cassava growth.
Planting and Maintenance
- Planting Time:The best time to plant cassava is during the rainy season, when moisture is readily available.
- Spacing:Space cassava plants 1-2 meters apart to allow for adequate air circulation and sunlight penetration.
- Watering:Water cassava plants regularly, especially during the initial stages of growth.
- Fertilization:Apply a balanced fertilizer every 2-3 months to ensure adequate nutrient supply for optimal growth.
- Weeding:Regularly remove weeds to prevent competition for nutrients and sunlight.
- Pest and Disease Control:Monitor cassava plants for pests and diseases and take appropriate control measures.
Propagation Methods
Cassava can be propagated through cuttings and seeds.
Cuttings
Cuttings are the most common method of propagation.
- Cuttings:Select healthy stems from mature cassava plants, ensuring each cutting has at least 3-4 nodes.
- Planting:Plant the cuttings directly into the soil, ensuring that the nodes are buried below the soil surface.
- Watering:Water the cuttings regularly to encourage root development.
Seeds
Cassava seeds are less commonly used for propagation due to their low germination rate.
- Seed Collection:Harvest mature cassava seeds from the plant’s capsules.
- Planting:Plant the seeds directly into the soil, ensuring that they are buried about 1-2 cm deep.
- Watering:Water the seeds regularly to maintain soil moisture.
Harvesting and Preserving Cassava Leaves
Harvesting cassava leaves at the optimal time ensures maximum nutritional value and a delicious, flavorful harvest. The ideal time to harvest cassava leaves is when they are young and tender, as they are at their peak in terms of nutrient content and flavor.
Harvesting Cassava Leaves
Harvesting cassava leaves is a straightforward process that requires minimal effort. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure a successful harvest:
- Choose the right leaves:Select the youngest and most tender leaves from the cassava plant. These leaves are typically found at the top of the plant and have a bright green color. Avoid harvesting leaves that are older, as they may be tougher and have a less desirable flavor.
- Cut the leaves:Use a sharp knife or scissors to cut the leaves at the base of the stem. This method helps to prevent damage to the plant and encourages new growth.
- Harvest in moderation:It is essential to harvest cassava leaves in moderation to ensure the plant’s health and continued growth. Aim to harvest only a few leaves at a time, leaving enough for the plant to thrive.
Preserving Cassava Leaves
Preserving cassava leaves allows you to enjoy their nutritional benefits and unique flavor throughout the year. Different preservation methods offer distinct advantages and are suitable for various preferences and storage conditions.
Drying Cassava Leaves
Drying cassava leaves is a traditional method of preservation that removes moisture, extending their shelf life. Here’s a detailed explanation of the process:
- Preparation:Wash the harvested cassava leaves thoroughly to remove any dirt or debris. Then, spread them out on a clean, dry surface or drying rack, ensuring good airflow.
- Drying:Dry the leaves in a well-ventilated area, preferably under direct sunlight. This method allows for natural drying and preserves the leaves’ flavor and nutrients. Alternatively, you can use a food dehydrator to dry the leaves at a controlled temperature, typically around 135°F (57°C).
- Storage:Once the leaves are completely dry and brittle, store them in airtight containers or resealable bags in a cool, dry place. This method helps to prevent moisture absorption and maintain the leaves’ quality.
Freezing Cassava Leaves
Freezing cassava leaves is a convenient and efficient way to preserve their freshness and nutrients for extended periods. This method involves blanching the leaves before freezing to maintain their color and texture.
- Blanching:Bring a large pot of water to a boil and add the washed cassava leaves. Blanch for 3-5 minutes, then immediately transfer them to a bowl of ice water to stop the cooking process. This step helps to retain the leaves’ vibrant color and prevents discoloration during freezing.
While cassava leaves offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, incorporating a touch of vibrant beauty to your garden can also enhance the overall experience. If you’re looking to add a splash of color and a touch of tropical flair, consider the stunning Jacaranda tree, known for its cascading purple blossoms.
For expert advice on cultivating this magnificent tree, check out our comprehensive guide: How to Use Jacaranda Tree for a Gorgeous Garden: Essential Growing and Care Tips. With a flourishing Jacaranda gracing your garden, you’ll have a beautiful backdrop to enjoy the benefits of your cassava leaf harvest.
- Packaging:After blanching, drain the leaves thoroughly and pack them into freezer-safe bags or containers. Squeeze out excess air from the bags to prevent freezer burn.
- Freezing:Place the packaged cassava leaves in the freezer and store them for up to 6 months. Ensure the leaves are frozen solid before stacking them to avoid damage.
Pickling Cassava Leaves
Pickling cassava leaves is a unique method of preservation that adds a tangy and flavorful twist to this nutritious green. Here’s a detailed explanation of the pickling process:
- Preparation:Wash and blanch the cassava leaves as described above. Then, chop them into smaller pieces for easier pickling.
- Brining:Combine a mixture of vinegar, salt, sugar, and spices in a large pot. Bring the mixture to a boil, then reduce the heat and simmer for 10-15 minutes. This creates a flavorful brine that will preserve the cassava leaves and enhance their taste.
- Pickling:Add the chopped cassava leaves to the simmering brine and cook for 5-10 minutes. Make sure the leaves are fully submerged in the brine. Once cooked, transfer the mixture to sterilized jars, leaving some space at the top. Seal the jars tightly and allow them to cool completely.
- Storage:Store the pickled cassava leaves in a cool, dark place for up to 6 months. Refrigerate them after opening the jars.
Culinary Uses of Cassava Leaves
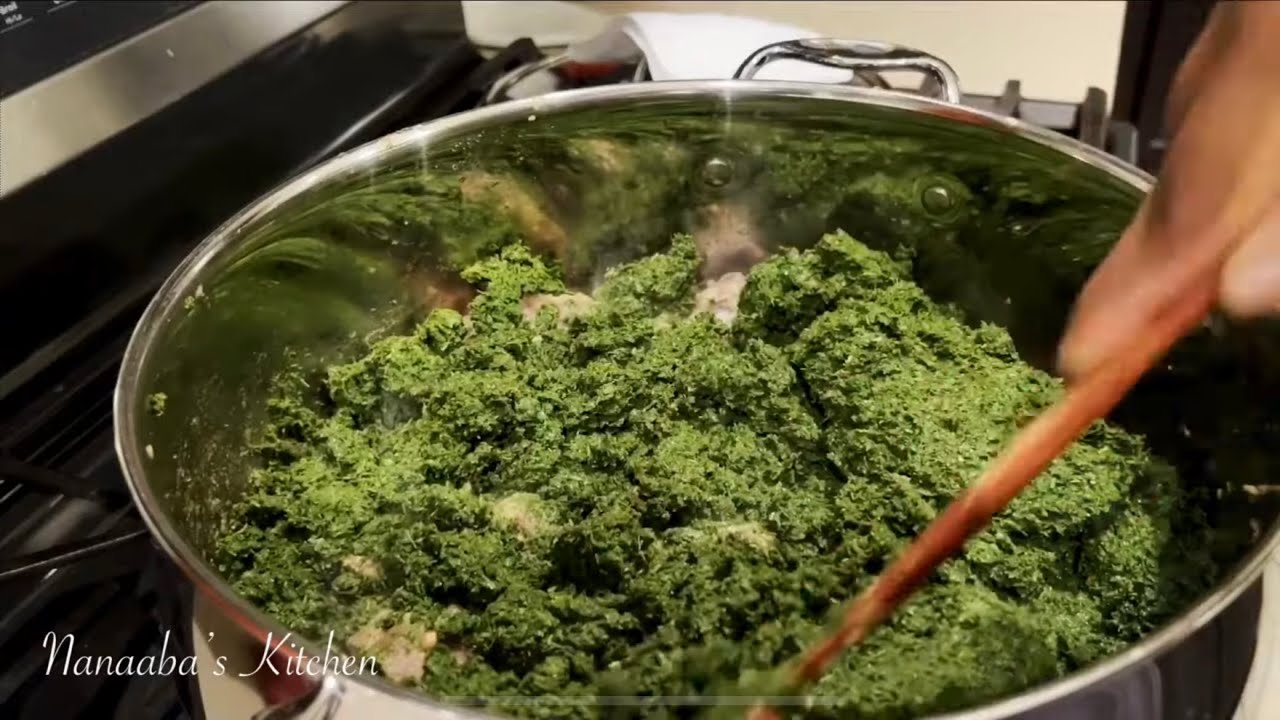
Cassava leaves, also known as “manihot” or “yuca” leaves, are a highly nutritious and versatile ingredient in various cuisines around the world. These leaves are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a valuable addition to your diet. Their unique flavor and texture lend themselves to a wide range of culinary applications, from traditional African dishes to modern Asian stir-fries.
Diverse Cassava Leaf Recipes
Cassava leaves are a staple ingredient in many cuisines, each with its own unique approach to preparing and incorporating them into dishes. Here’s a glimpse into the diverse world of cassava leaf recipes:
Culture |
Dish Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
West African |
Egusi Soup |
A rich and flavorful soup featuring ground melon seeds, cassava leaves, and various meats or fish. |
Nigerian |
Afang Soup |
A hearty soup with a distinctive aroma and flavor, made with afang leaves, waterleaf, and cassava leaves. |
Southeast Asian |
Stir-fried Cassava Leaves |
A simple yet flavorful dish with cassava leaves stir-fried with garlic, ginger, and chili peppers. |
Brazilian |
Caruru |
A traditional dish with cassava leaves cooked in a rich peanut sauce, often served with seafood. |
Filipino |
Ginataan |
A coconut milk-based dish featuring cassava leaves, shrimp, and vegetables. |
Preparing and Cooking Cassava Leaves
Cassava leaves are a delicate ingredient that requires careful preparation to ensure optimal flavor and texture. Here are some tips for preparing and cooking cassava leaves:* Remove the tough stems:Before cooking, remove the tough stems from the cassava leaves. This can be done by simply pulling them off or by using a sharp knife.
Cassava leaf magic isn’t just about the plant itself, but also about the culinary creativity it inspires. Just as cassava leaves can be transformed into delicious dishes, other exotic ingredients like kaffir lime leaves can add unique flavors to your meals.
For tips on incorporating this aromatic citrus leaf into your cooking, check out The Art of Cooking with Kaffir Lime Leaf: Essential Tips for Flavorful Meals. Whether you’re experimenting with cassava leaves or exploring new flavor profiles, remember that culinary adventures often lead to delicious discoveries.
Blanch the leaves
Blanching the leaves in boiling water for a few minutes helps to soften them and remove any bitterness.
Cook with other ingredients
Cassava leaves are best cooked with other ingredients, such as meats, fish, vegetables, or spices, to enhance their flavor.
Avoid overcooking
Overcooked cassava leaves can become mushy and lose their flavor. Cook them until tender but still slightly crisp.
Preparing a Popular Cassava Leaf Dish: Egusi Soup
Egusi soup is a popular West African dish that features cassava leaves as a key ingredient. Here’s a step-by-step guide for preparing this flavorful soup:
1. Prepare the ingredients
Gather your ingredients, including ground melon seeds, cassava leaves, beef or chicken, onions, tomatoes, peppers, and spices.
2. Cook the meat
In a large pot, add the meat and water and bring to a boil. Reduce heat and simmer until the meat is tender.
3. Sauté the vegetables
In a separate pan, sauté the onions, tomatoes, and peppers until softened.
4. Add the melon seeds
Add the ground melon seeds to the sautéed vegetables and cook for a few minutes, stirring constantly.
5. Combine the ingredients
Add the sautéed mixture and the cooked meat to the pot with the meat broth. Bring to a boil, then reduce heat and simmer for 15-20 minutes.
6. Add the cassava leaves
Add the blanched cassava leaves to the soup and cook for 5-10 minutes, or until tender.
7. Season to taste
Season the soup with salt, pepper, and other desired spices.
8. Serve
Serve the egusi soup hot with fufu, pounded yam, or rice.
Health Benefits of Consuming Cassava Leaves
Cassava leaves, often overlooked as a food source, are a nutritional powerhouse packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Regular consumption of these leafy greens can significantly contribute to overall health and well-being.
Nutritional Composition of Cassava Leaves
Cassava leaves are an excellent source of various nutrients, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. They are particularly rich in:
- Vitamins:Cassava leaves are abundant in vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and several B vitamins, including thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and folate. These vitamins play crucial roles in supporting immune function, vision, cell growth, and energy production.
- Minerals:They are a good source of minerals like iron, calcium, potassium, and magnesium. Iron is essential for red blood cell production, calcium for bone health, potassium for blood pressure regulation, and magnesium for muscle function and nerve health.
- Protein:Cassava leaves provide a decent amount of protein, making them a valuable source for vegetarians and vegans. Protein is vital for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting overall growth and development.
- Fiber:Cassava leaves are rich in dietary fiber, which aids digestion, promotes satiety, and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Antioxidants:Cassava leaves contain various antioxidants, including flavonoids and carotenoids. These compounds protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Health Benefits of Consuming Cassava Leaves
The rich nutritional profile of cassava leaves translates into numerous health benefits. Regular consumption of these leafy greens has been linked to:
- Improved Immune Function:The high vitamin C content in cassava leaves strengthens the immune system, enhancing the body’s ability to fight off infections and diseases.
- Enhanced Vision:The presence of vitamin A contributes to maintaining healthy vision, reducing the risk of night blindness and other eye conditions.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control:The fiber content in cassava leaves helps regulate blood sugar levels, making them beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
- Reduced Risk of Heart Disease:The potassium and fiber in cassava leaves help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Improved Bone Health:The calcium content in cassava leaves supports bone health, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Anti-Cancer Properties:The antioxidants in cassava leaves have been shown to possess anti-cancer properties, protecting cells from damage and reducing the risk of certain types of cancer.
- Improved Anemia:The iron content in cassava leaves can help treat and prevent anemia, a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells.
Comparison of Cassava Leaves with Other Leafy Green Vegetables, Cassava Leaf Magic: How to Cultivate and Enjoy This Nutritious Green for Optimal Results
Cassava leaves share a similar nutritional profile with other leafy green vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collard greens. However, they differ in certain aspects:
- Vitamin A:Cassava leaves are a richer source of vitamin A than spinach, kale, and collard greens.
- Iron:Cassava leaves contain more iron than spinach, but less than kale and collard greens.
- Calcium:Cassava leaves have a lower calcium content compared to spinach, kale, and collard greens.
- Fiber:Cassava leaves have a higher fiber content than spinach and kale but less than collard greens.
Recipes and Culinary Ideas
Cassava leaves, often referred to as “cassava greens” or “Manihot leaves,” offer a wide range of culinary possibilities. They are a staple ingredient in many African, South American, and Caribbean cuisines, and their versatility allows them to be incorporated into various dishes, from traditional stews and soups to modern salads and stir-fries.
Cassava Leaf Recipes
Cassava leaves are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a nutritious addition to your diet. Here are a few popular recipes featuring cassava leaves as a primary ingredient:
- Cassava Leaf Soup (Egusi Soup):A popular West African soup, Egusi soup typically includes ground melon seeds (egusi), meat or fish, vegetables like spinach or bitter leaf, and cassava leaves. The cassava leaves add a unique flavor and texture to the soup, and their nutritional value enhances the dish’s overall health benefits.
- Cassava Leaf Stew (Spinach Stew):A simple and flavorful stew, cassava leaves are often cooked with tomatoes, onions, garlic, and spices like paprika and cayenne pepper. This stew can be served with rice, fufu, or plantains, making it a satisfying and nutritious meal.
- Cassava Leaf Salad:A refreshing and healthy salad, cassava leaves can be blanched and combined with other ingredients like tomatoes, onions, cucumbers, and a light vinaigrette. This salad is a great way to enjoy the unique flavor and texture of cassava leaves while incorporating other nutritious vegetables.
Cassava Leaves in Different Cuisines
Cassava leaves are widely used in various cuisines worldwide, demonstrating their culinary versatility.
- African Cuisine:In West Africa, cassava leaves are a staple ingredient in soups, stews, and sauces. They are often used in dishes like Egusi soup, okra soup, and vegetable stew.
- South American Cuisine:In Brazil, cassava leaves are commonly used in dishes like “Maniçoba,” a traditional stew made with cassava leaves, meat, and other vegetables.
- Caribbean Cuisine:In the Caribbean, cassava leaves are used in dishes like “Callaloo,” a traditional soup made with cassava leaves, spinach, and other vegetables.
Last Word
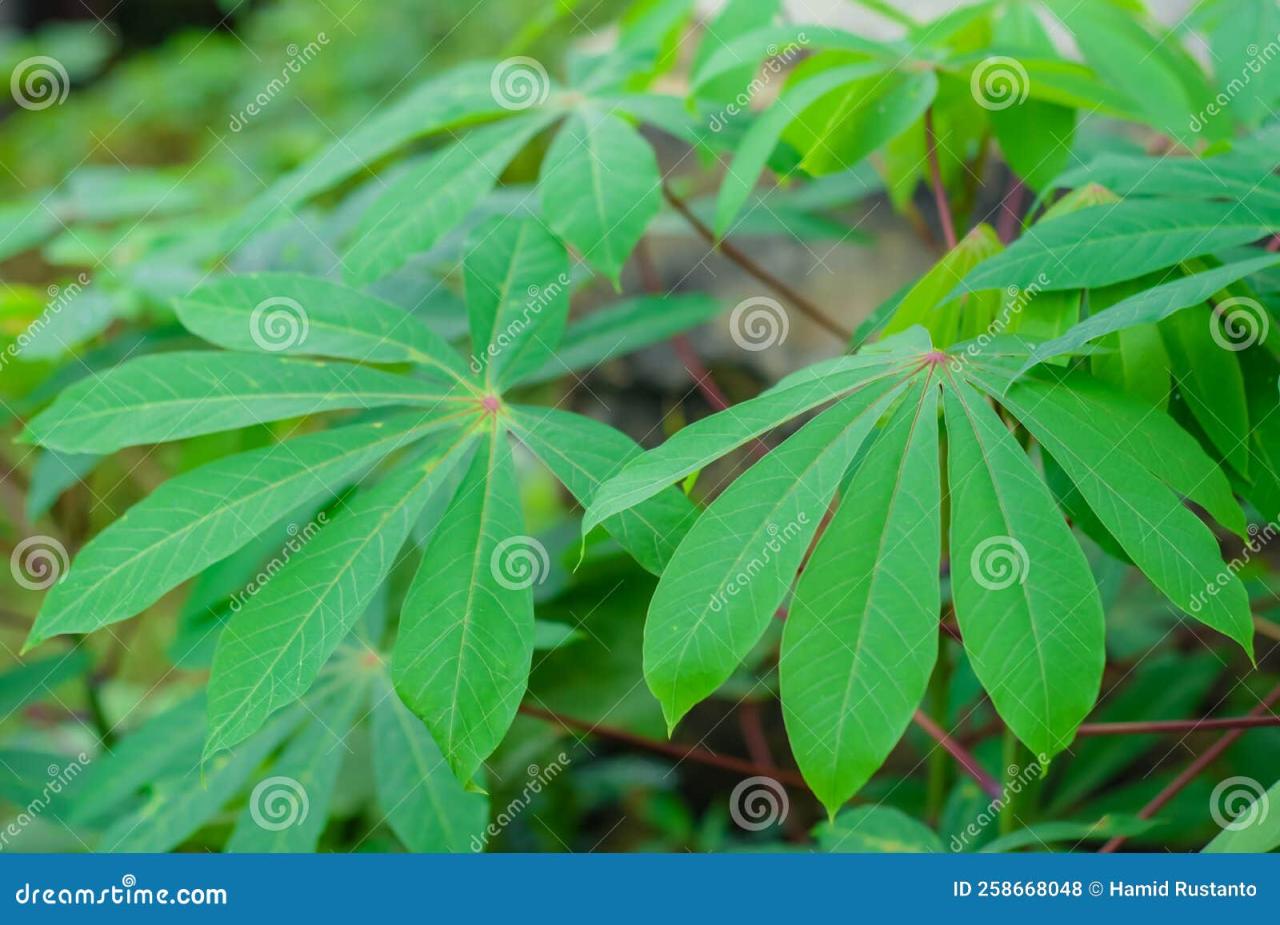

Harnessing the magic of cassava leaf involves more than just appreciating its culinary versatility. It’s about embracing a sustainable approach to gardening, understanding the nuances of its cultivation, and appreciating the profound impact this humble green can have on our health and well-being.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a culinary enthusiast, exploring the world of cassava leaf opens a door to a nutritious and flavorful journey. By understanding its cultivation, harvesting, and culinary applications, we can unlock the full potential of this remarkable green, transforming it from a humble plant into a vibrant addition to our kitchens and lives.
FAQs: Cassava Leaf Magic: How To Cultivate And Enjoy This Nutritious Green For Optimal Results
Is cassava leaf safe to eat?
Yes, cassava leaves are safe to eat when properly prepared. They are a nutritious food source rich in vitamins and minerals. However, it’s crucial to properly cook them to remove any toxins that may be present.
Can I grow cassava leaves in my backyard?
Yes, cassava leaves can be grown in a variety of climates, but they thrive in warm, tropical environments. Ensure your soil is well-drained and receives ample sunlight.
Are cassava leaves good for weight loss?
Cassava leaves are low in calories and high in fiber, which can contribute to a feeling of fullness and aid in weight management. However, it’s important to note that no single food can guarantee weight loss.
What are some common ways to prepare cassava leaves?
Cassava leaves can be boiled, steamed, sautéed, or used in soups, stews, and salads. They are often combined with other vegetables and spices to create flavorful dishes.
Where can I find cassava leaves?
Cassava leaves are available at some Asian and African markets. You can also find them online or at specialty food stores. If you have access to a tropical climate, you can grow your own cassava plants.
